It was the capstone project of my undergraduate program. I cooperated with Yuan Feng, designed and developed the whole game system. I was mainly responsible for the research process, physical product design and the initial idea of the game planning, while Yuan was responsible for coding and development. After my graduation, we cooperated with two fellow students to write essay of this project. And the essay was accepted for HCII2018 Conference.
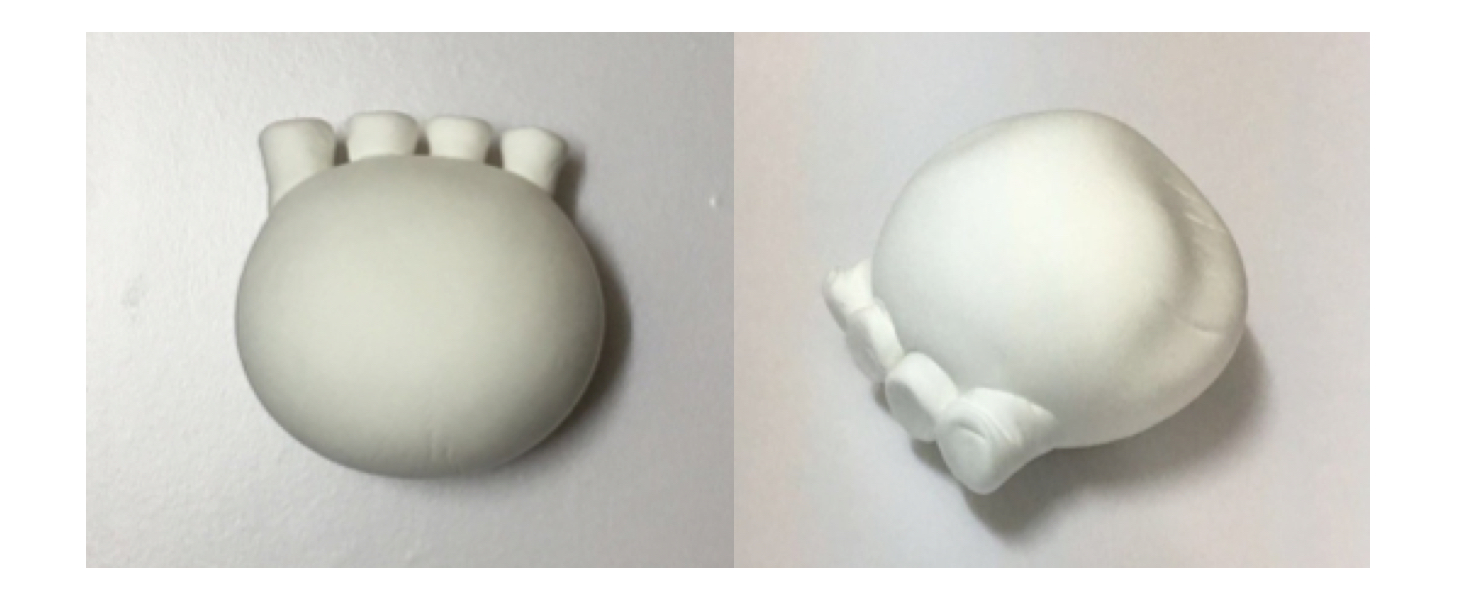
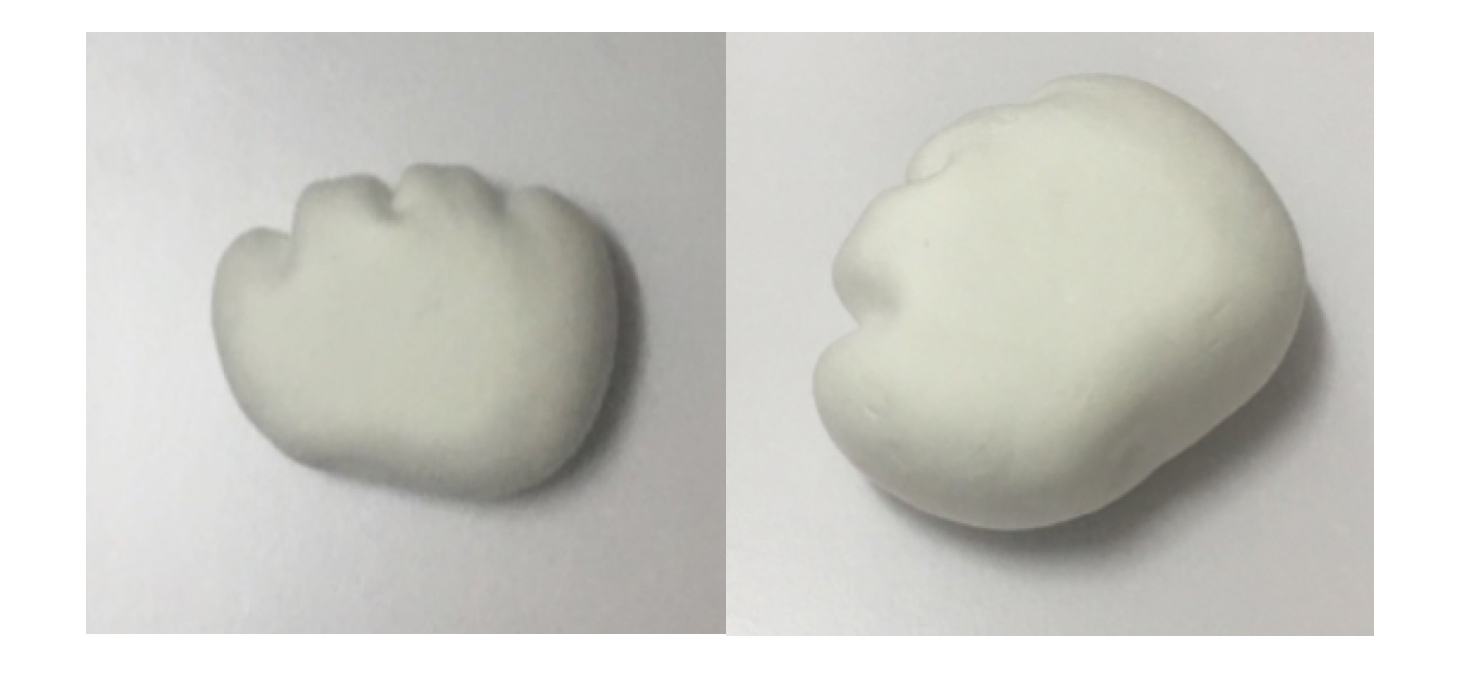
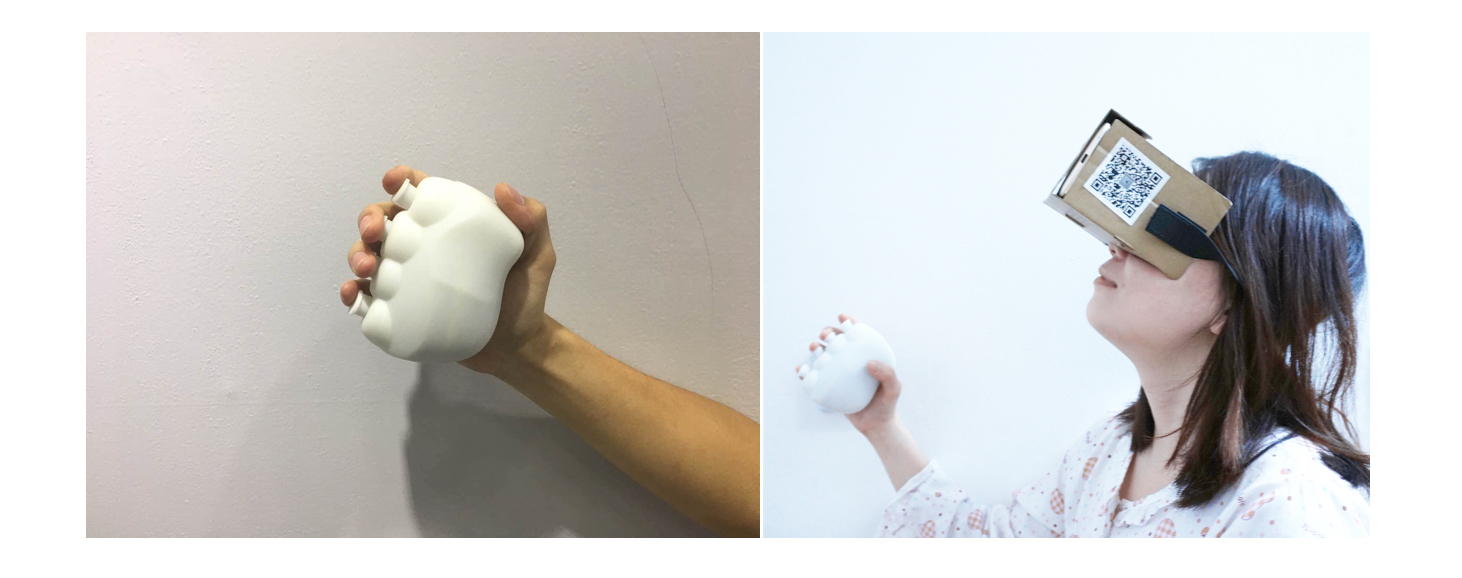
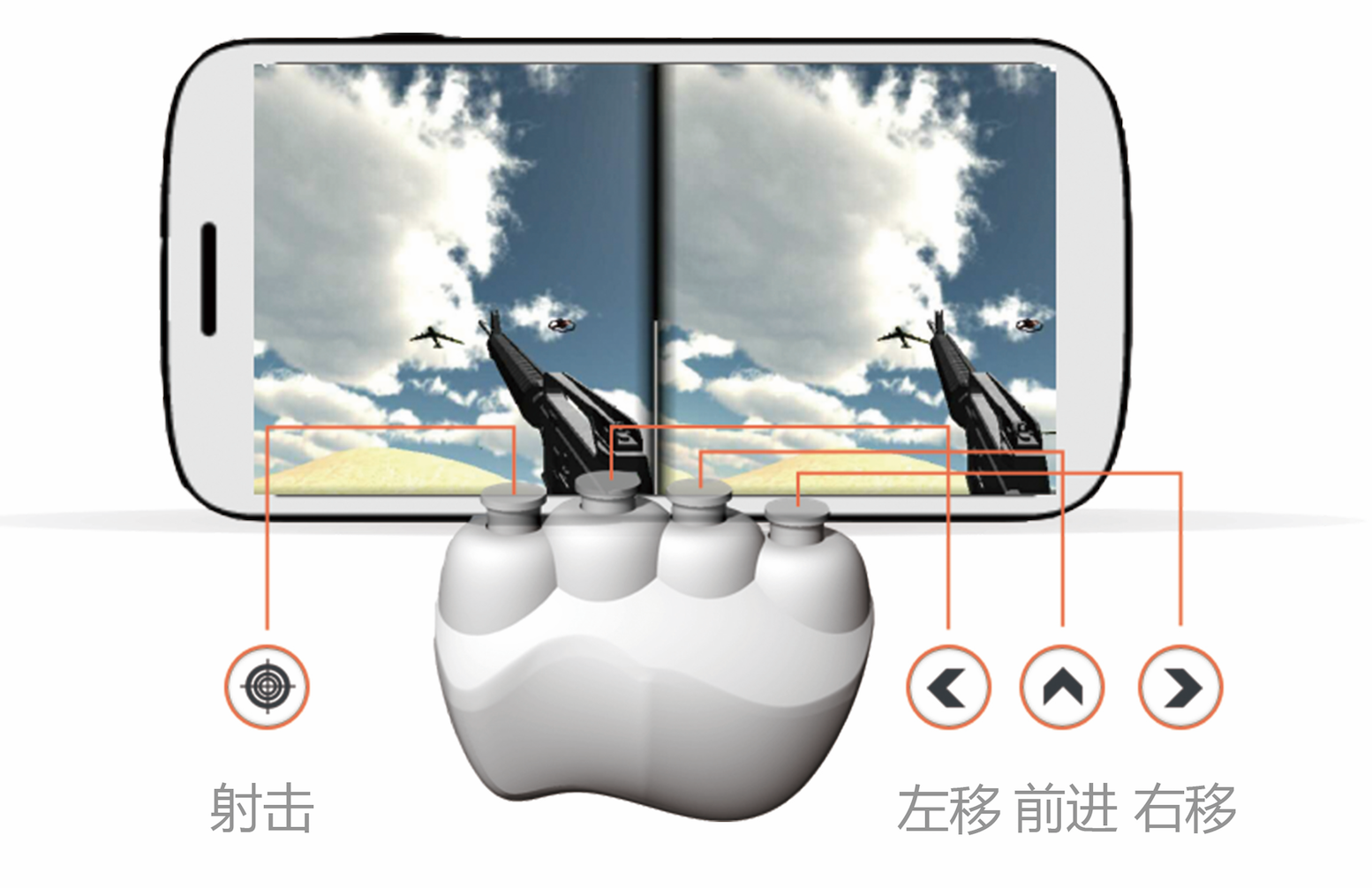
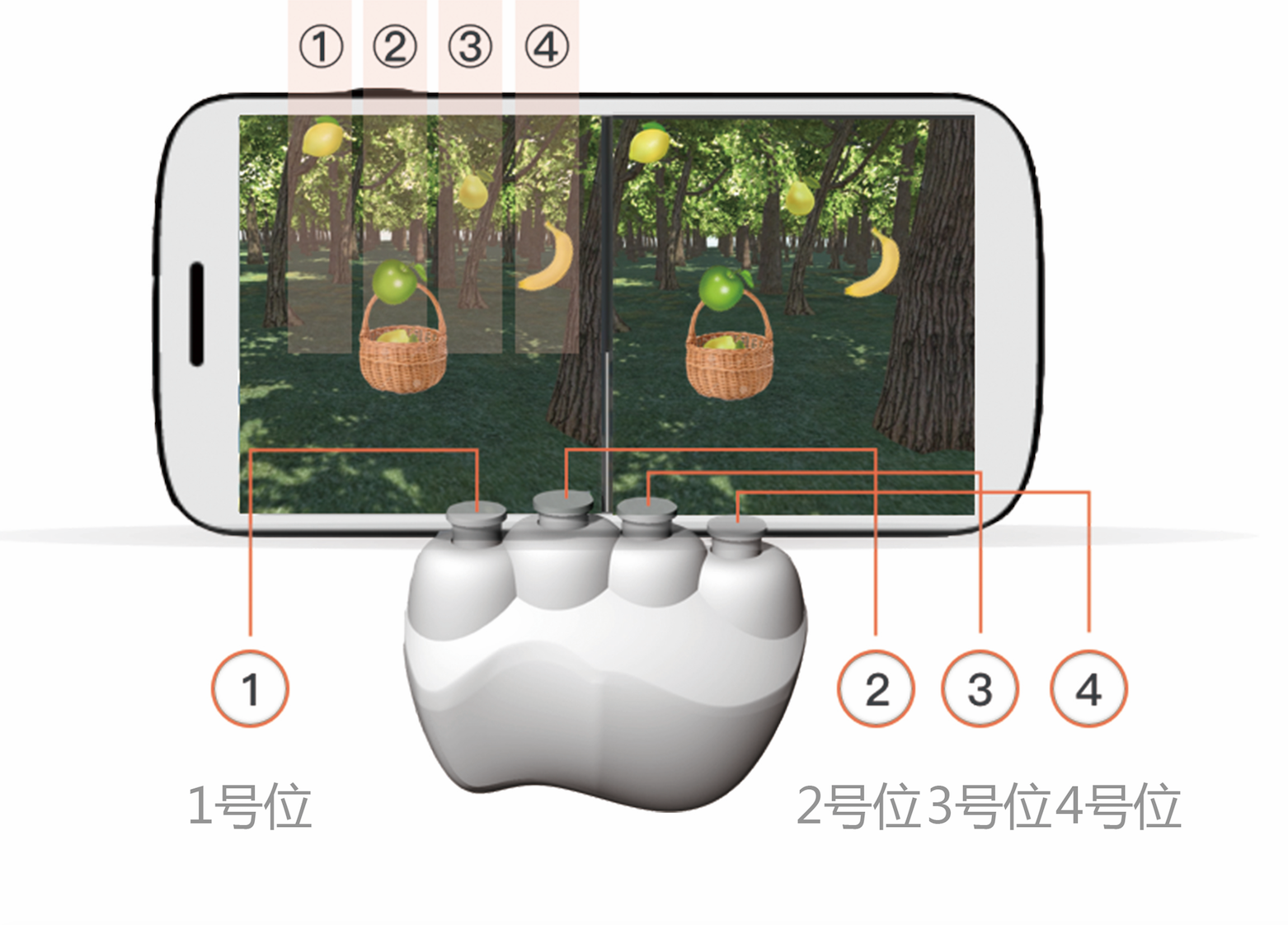
This project studies the combination of virtual reality (VR) technology and conventional stroke rehabilitation physiotherapy. Specifically, we propose a novel therapeutic device coupled with an immersive VR software environment to foster hand rehabilitation.
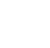
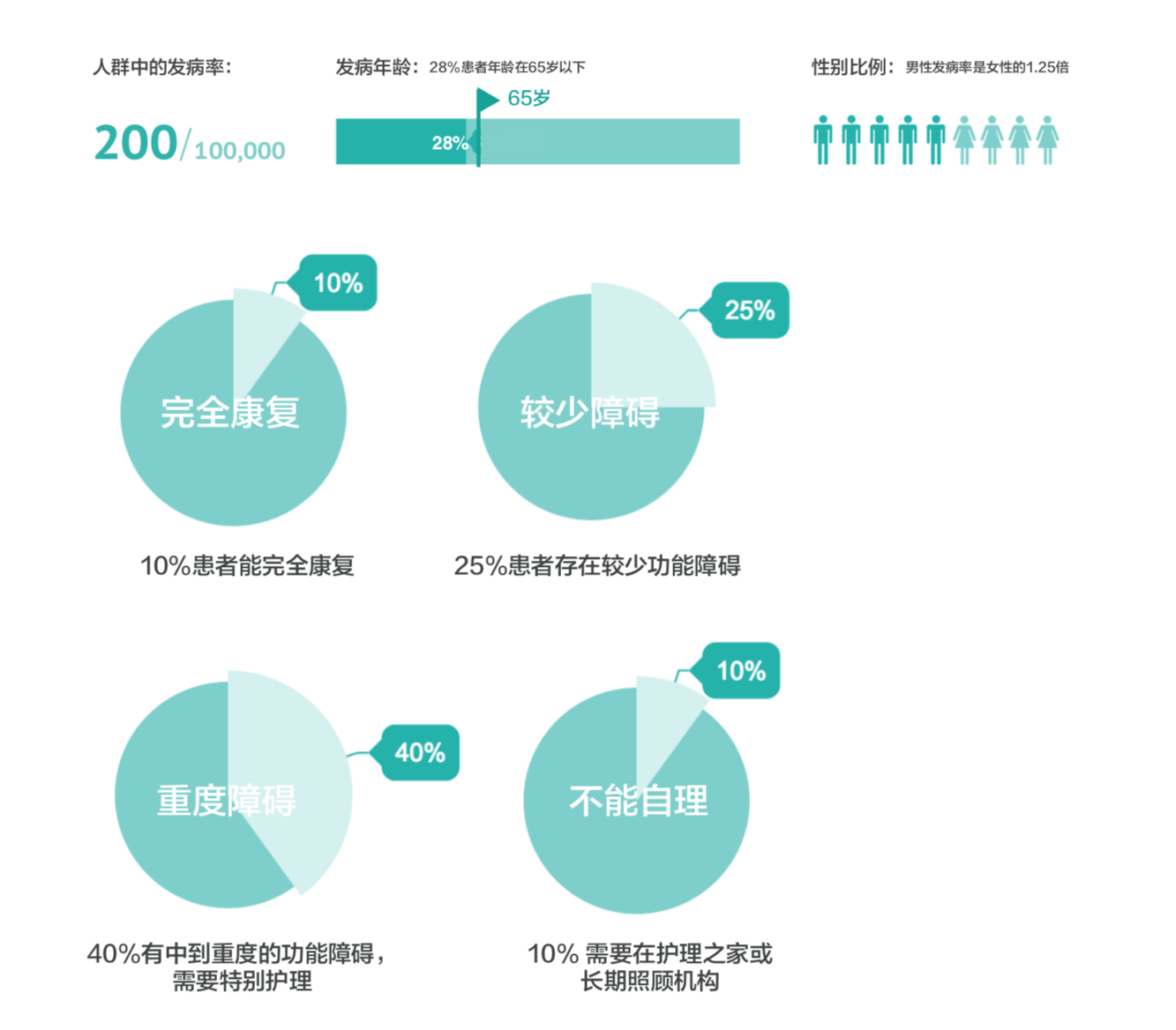
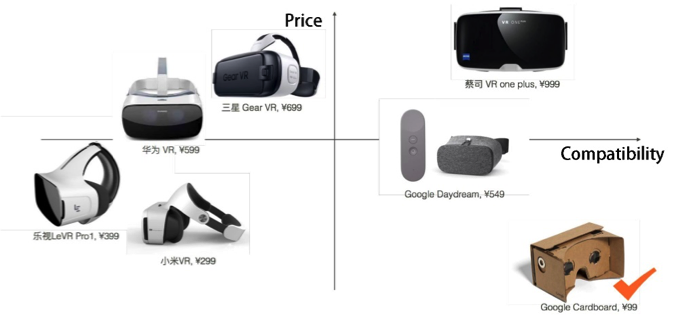
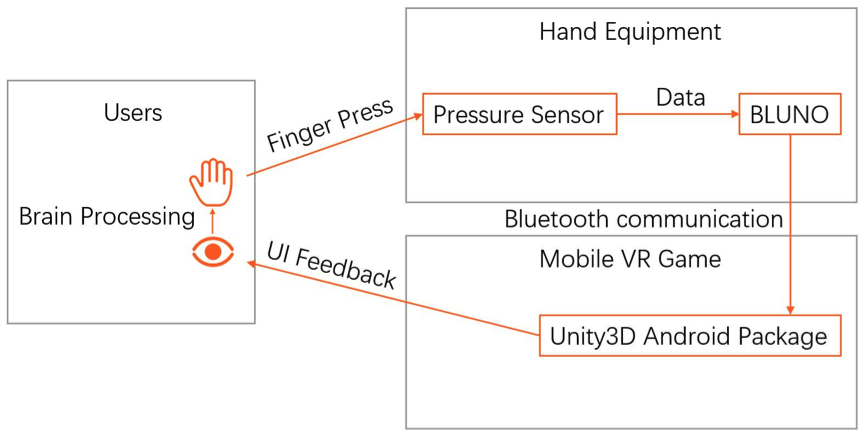
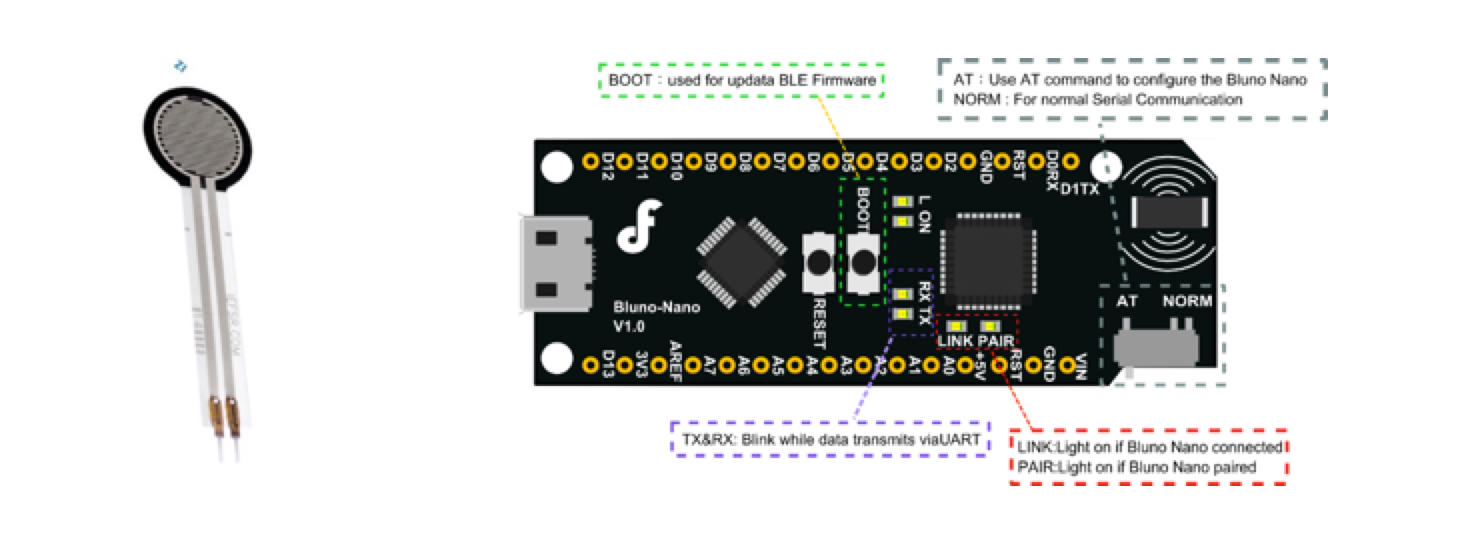
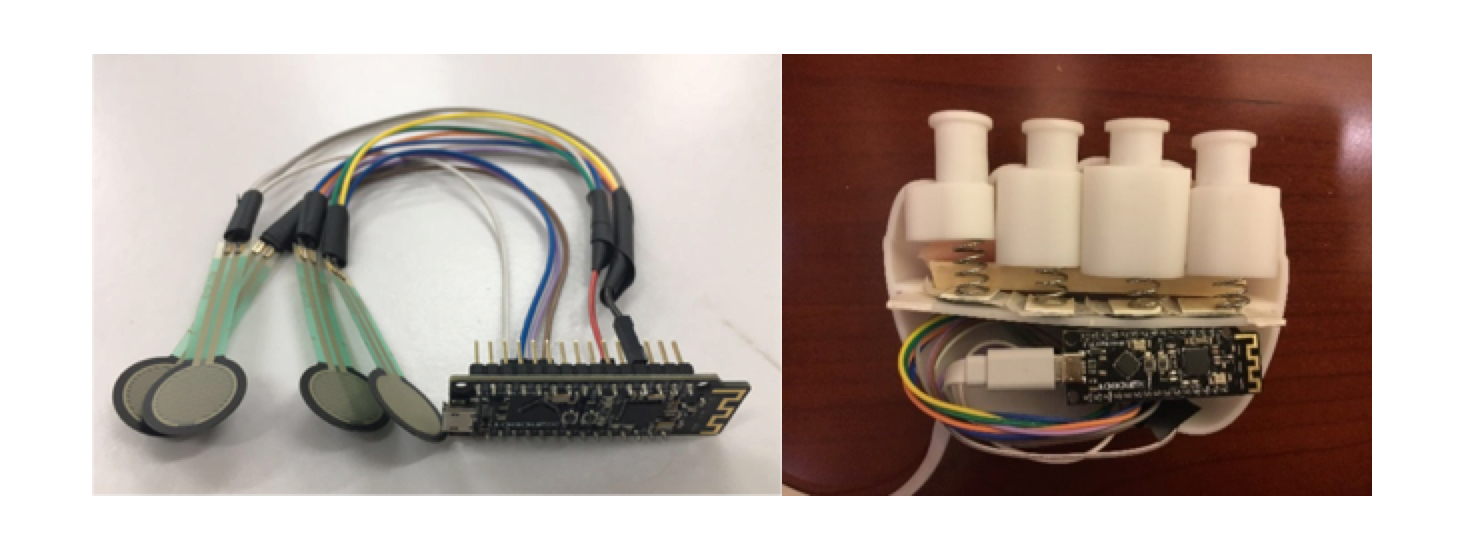
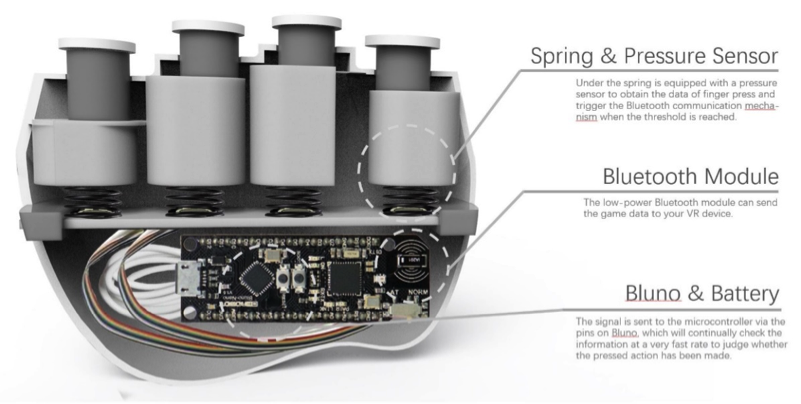
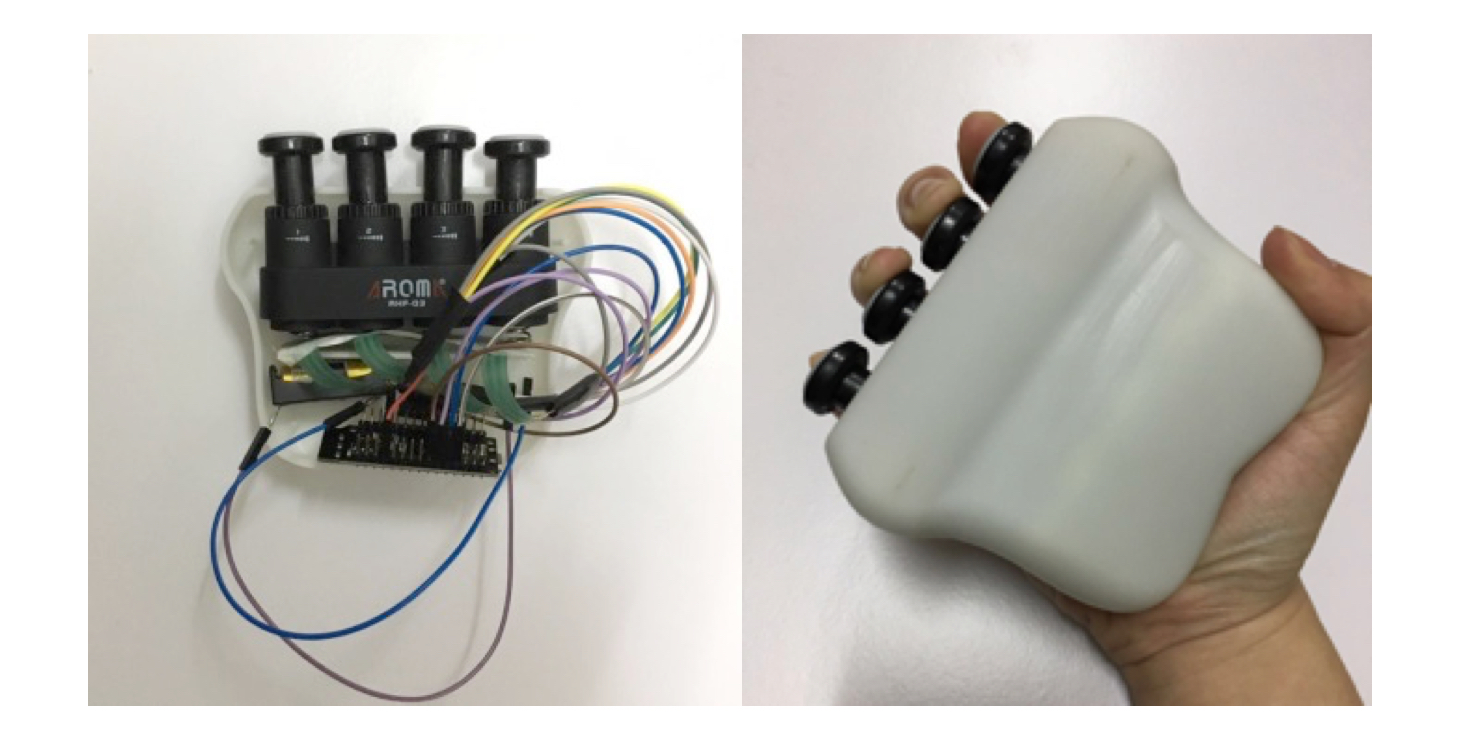
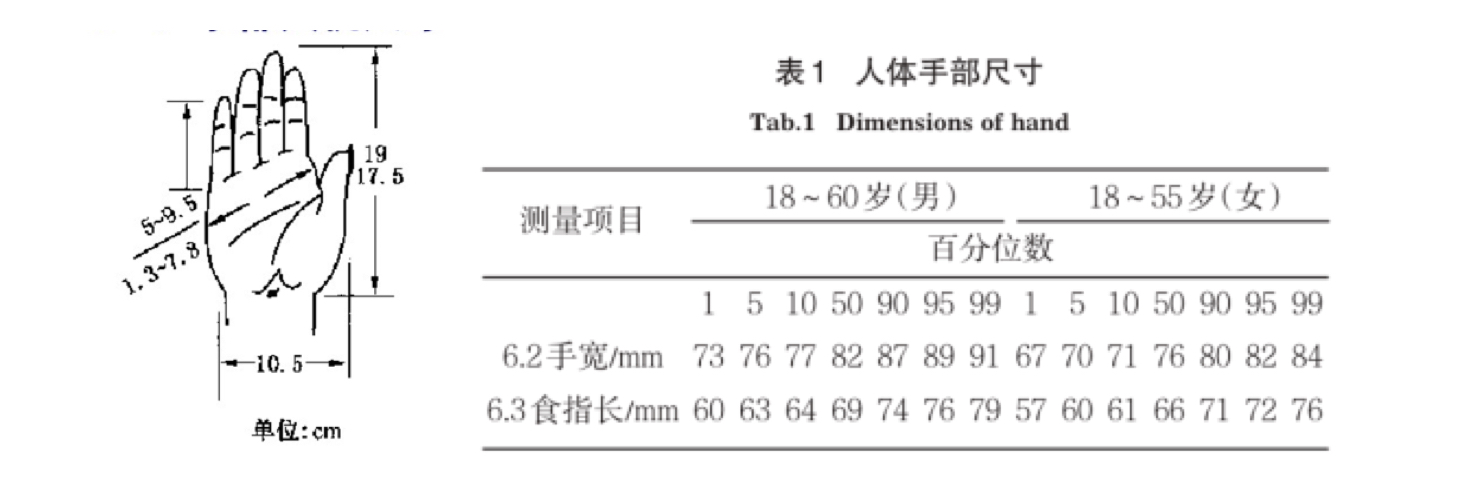
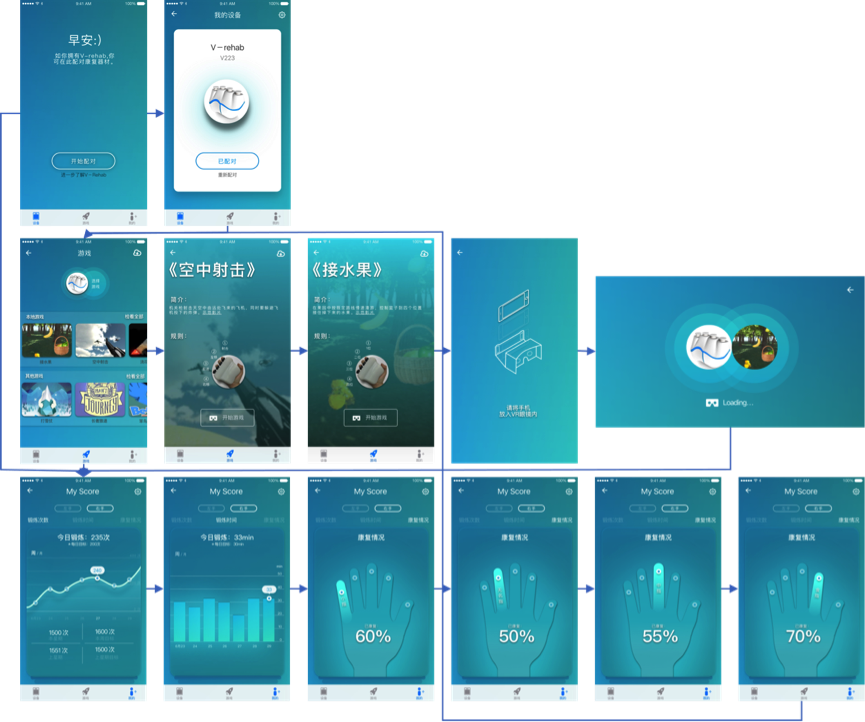
We first study the current state of the art in VR technology use in medical rehabilitation. Next, we investigate the conventional stroke rehabilitation process to integrate accepted methods of physical therapy into mobile games. The game system’s input device (V-rehab) is an improvement on existing rehabilitation equipment, designed to maximize interaction between user and game. We feature a prototype game system based on sensor hardware and a custom environment running on the Unity3D software platform. Finally, we show results of system testing and discuss the application of VR in stroke rehabilitation.